Vertebral Subluxation and Systems Biology: An Integrative Review Exploring the Salutogenic Influence of Chiropractic Care on the Neuroendocrine-Immune System
Vertebral Subluxation and Systems Biology: An Integrative Review Exploring the Salutogenic Influence of Chiropractic Care on the Neuroendocrine-Immune System
SOURCE: Cureus 2024 (Mar 15); 16 (3): e56223
| OPEN ACCESS |
Amy Haas • Jonathan Chung • Christopher Kent • Brooke Mills and Matthew McCoy
Foundation for Vertebral Subluxation
4390 Bells Ferry Road
Kennesaw, Georgia 30144
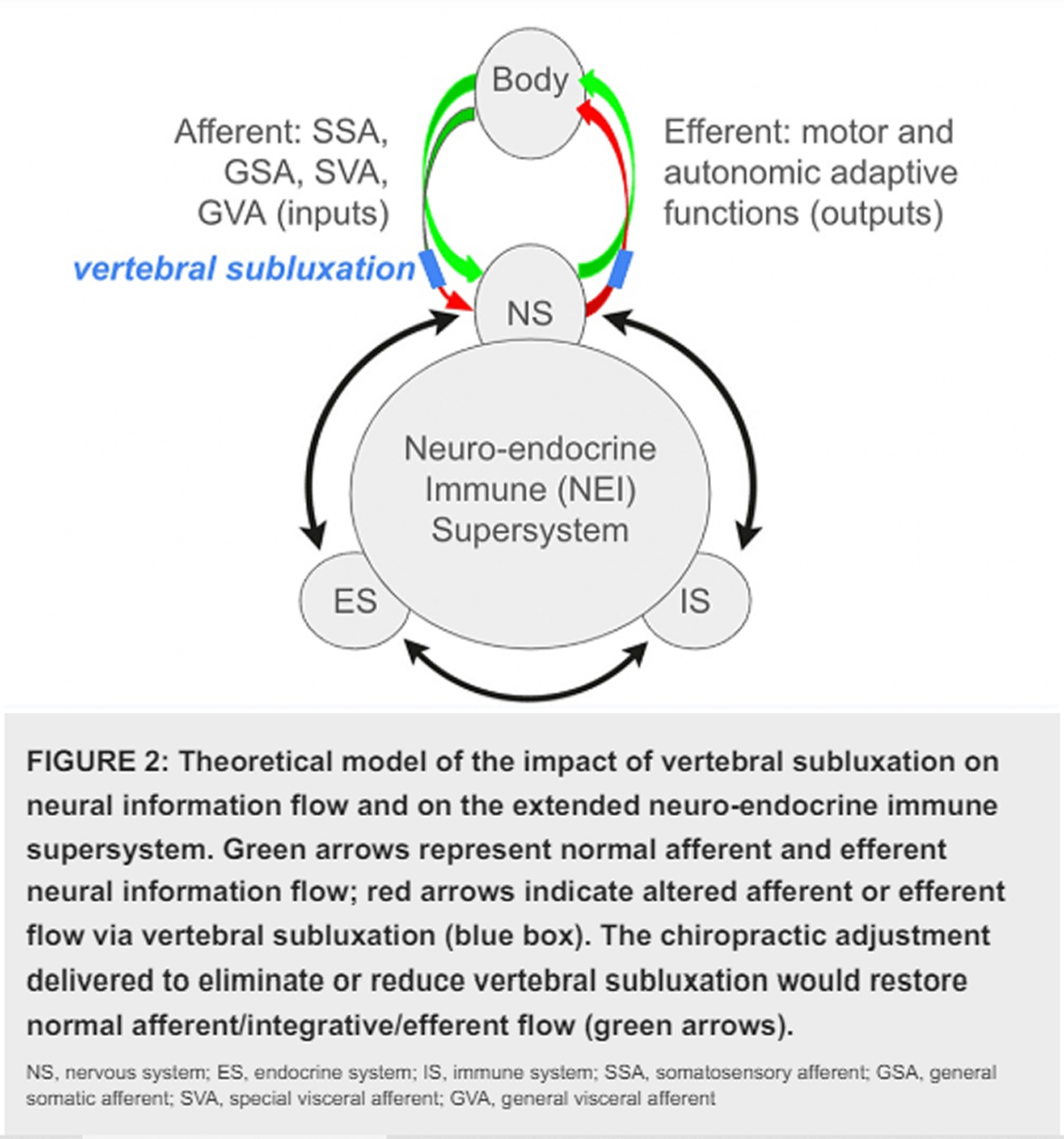
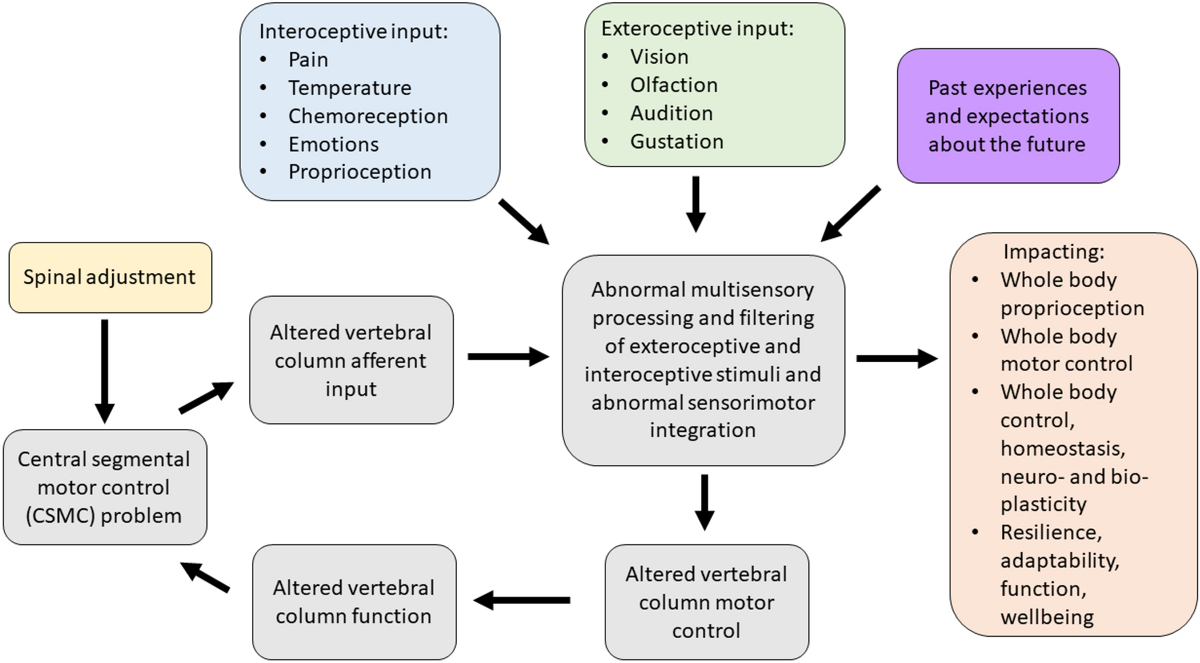
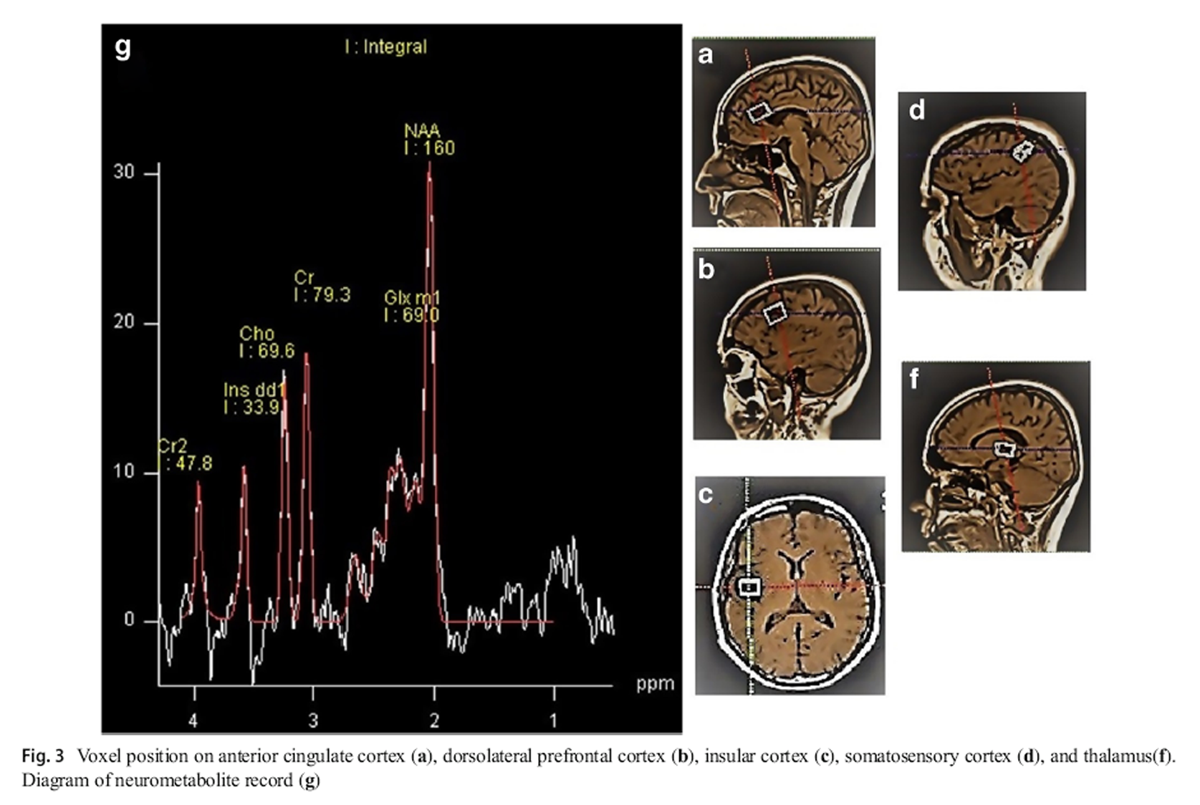
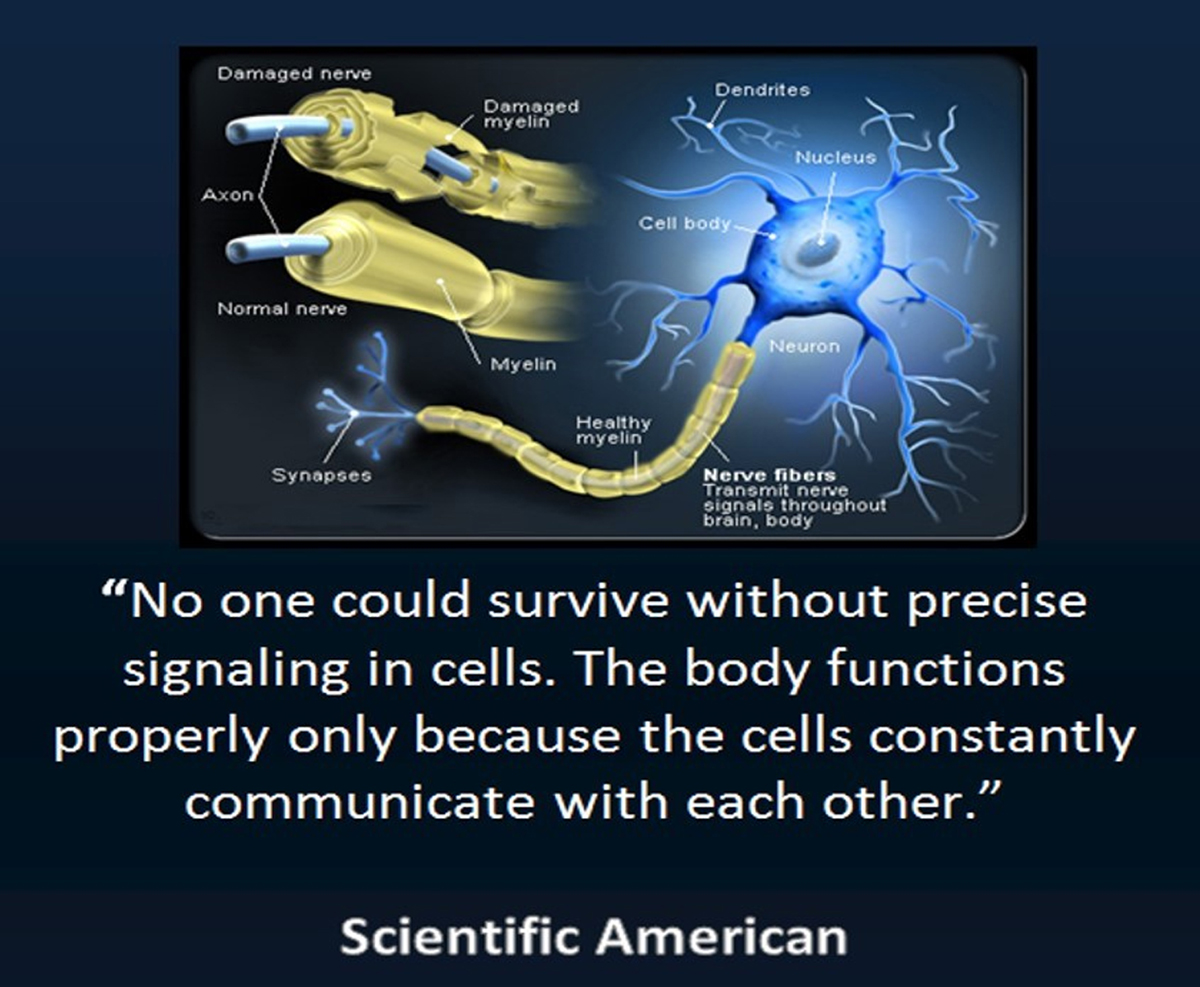
In this paper we synthesize an expansive body of literature examining the multifaceted influence of chiropractic care on processes within and modulators of the neuroendocrine-immune (NEI) system, for the purpose of generating an inductive hypothesis regarding the potential impacts of chiropractic care on integrated physiology. Taking a broad, interdisciplinary, and integrative view of two decades of research-documented outcomes of chiropractic care, inclusive of reports ranging from systematic and meta-analysis and randomized and observational trials to case and cohort studies, this review encapsulates a rigorous analysis of research and suggests the appropriateness of a more integrative perspective on the impact of chiropractic care on systemic physiology. A novel perspective on the salutogenic, health-promoting effects of chiropractic adjustment is presented, focused on the improvement of physical indicators of well-being and adaptability such as blood pressure, heart rate variability, and sleep, potential benefits that may be facilitated through multiple neurologically mediated pathways. Our findings support the biological plausibility of complex benefits from chiropractic intervention that is not limited to simple neuromusculoskeletal outcomes and open new avenues for future research, specifically the exploration and mapping of the precise neural pathways and networks influenced by chiropractic adjustment.
There are more articles like this @