Association Between Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation and Cauda Equina Syndrome in Adults With Low Back Pain: Retrospective Cohort Study of US Academic Health Centers
Association Between Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation and Cauda Equina Syndrome in Adults With Low Back Pain: Retrospective Cohort Study of US Academic Health Centers
SOURCE: PLoS One 2024 (Mar 11); 19 (3): e0299159
Robert J. Trager • Anthony N. Baumann • Jaime A. Perez
Jeffery A. Dusek • Romeo-Paolo T. Perfecto • Christine M. Goertz
Connor Whole Health,
University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center,
Cleveland, Ohio, United States of America.
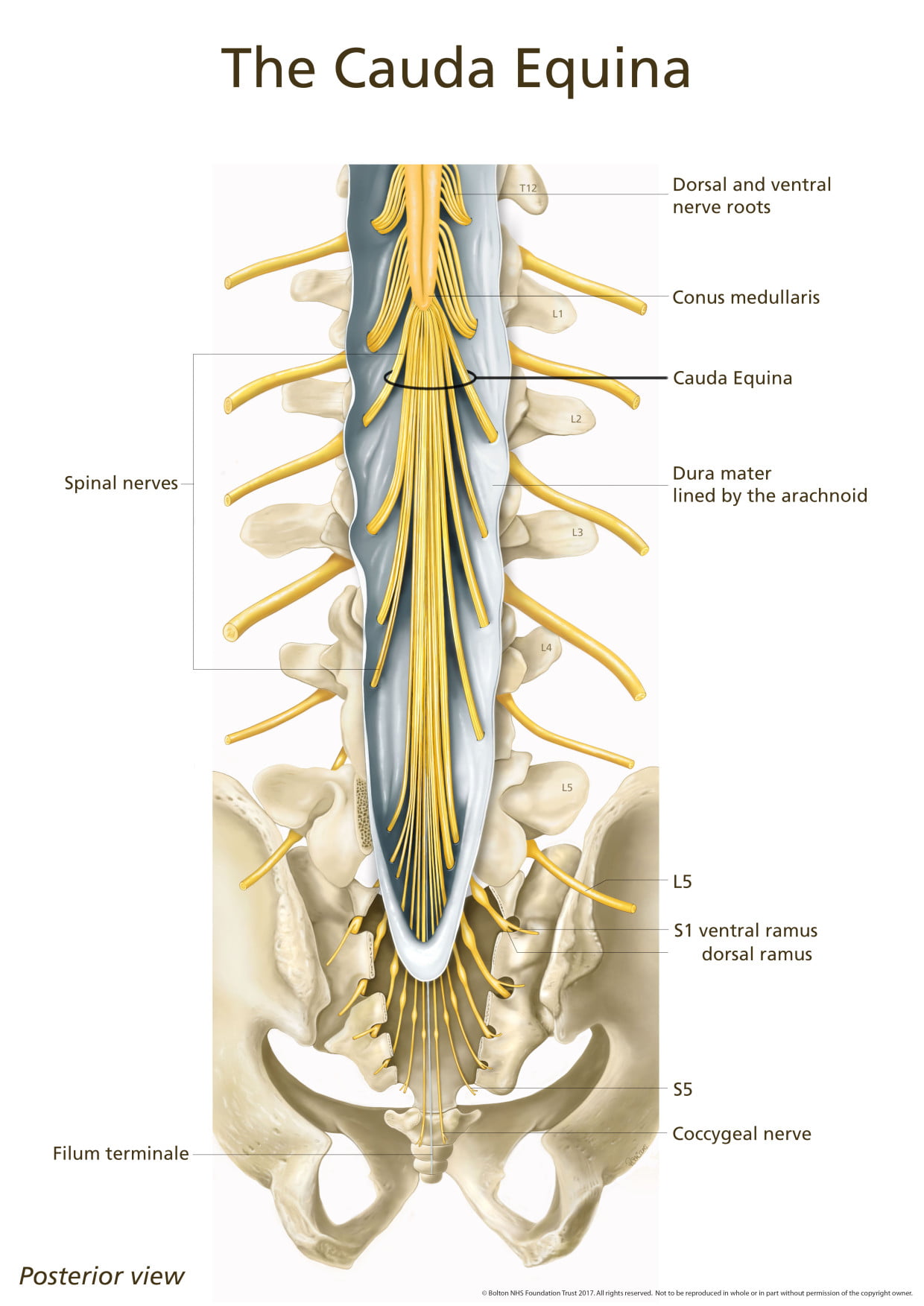
Background: Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a lumbosacral surgical emergency that has been associated with chiropractic spinal manipulation (CSM) in case reports. However, identifying if there is a potential causal effect is complicated by the heightened incidence of CES among those with low back pain (LBP). The study hypothesis was that there would be no increase in the risk of CES in adults with LBP following CSM compared to a propensity-matched cohort following physical therapy (PT) evaluation without spinal manipulation over a three-month follow-up period.
Methods: A query of a United States network (TriNetX, Inc.) was conducted, searching health records of more than 107 million patients attending academic health centers, yielding data ranging from 20 years prior to the search date (July 30, 2023). Patients aged 18 or older with LBP were included, excluding those with pre-existing CES, incontinence, or serious pathology that may cause CES.
Patients were divided into two cohorts:
(2) LBP patients receiving PT evaluation without spinal manipulation.
There are more articles like this @