Lower Back Trauma (Lumbar Spine and Pelvis)
By R. C. Schafer, DC, PhD, FICC
Although it may be easier to teach anatomy by dividing the body into arbitrary parts, a misinterpretation can be created. For instance, we find clinically that the lumbar spine, sacrum, ilia, pubic bones, and hips work as a functional unit. Any disorder of one part immediately affects the function of the other parts. We should also keep in mind that an axial kinematic chain of weight-supporting segments extends from the occipital base to the soles of the feet.
Because the number of professional papers concerning the cause and diagnosis of low-back pain is voluminous, emphasis herein is placed on points that the author believes are important but not often emphasized in popular literature.
BACKGROUND
A wide assortment of muscle, tendon, ligament, bone, nerve, and vascular injuries in this area is witnessed during posttrauma care. As with other areas of the body, the first step in the posttrauma examination process is knowing the mechanism of injury if possible. Evaluation can be rapid and accurate with this knowledge.
Low-back disability rapidly demotivates productivity and athletic participation. The mechanism of injury is usually intrinsic rather than extrinsic. The cause can often be through overbending, a heavy steady lift, or a sudden release –all which primarily involve the muscles. IVD disorders are more often, but not exclusively, attributed to extrinsic blows and intrinsic wrenches. An accurate and complete history is invariably necessary to offer the best management and counsel.
Initial Assessment
A player injured on the field or a worker injured in the shop should never be moved until emergency assessment is completed. Once severe injury has been eliminated, transfer to a backboard can be made and further evaluation conducted at an aid station.
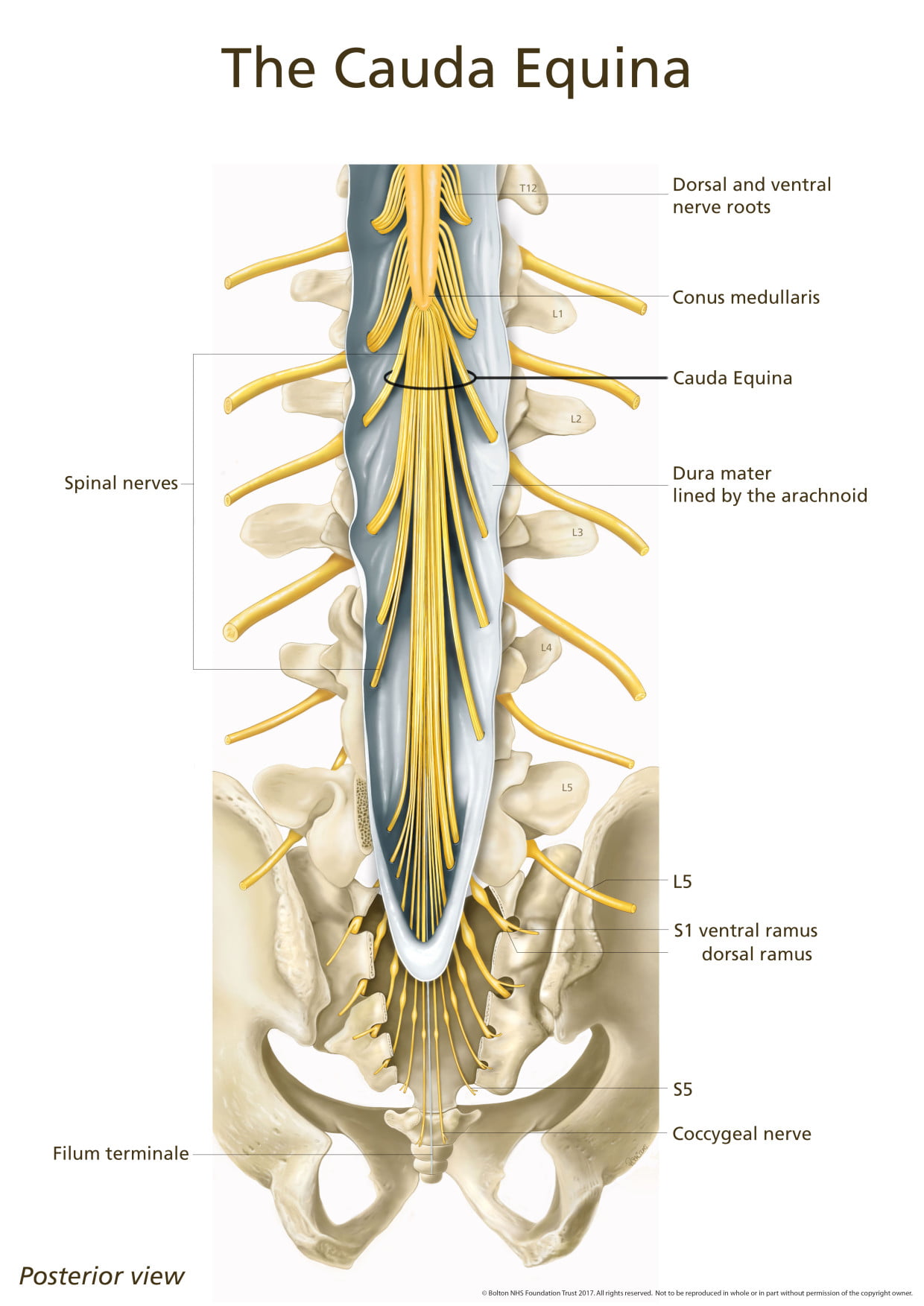
Neurologic Levels
Neurologic assessment should be made as soon as logical. Muscle tonus (flaccidity, rigidity, spasticity) by passive movements is determined. Voluntary power of each suspected group of muscles against resistance is tested, and the force is compared bilaterally. Check pupil size, ability to follow finger motion, and reaction to light. Cremasteric (L1–L2), patellar (L2–L4), gluteal (L4–S1), suprapatellar, Achilles (L5–S2), plantar (S1–S2), and anal (S5–Cx1) reflexes are evaluated. Patellar and ankle clonuses are noted. Coordination and sensation by gait, heel-to-knee and foot-to-buttock tests, and Romberg’s station test are checked. These are typical minimal evaluations.
Initial Assessment
Tenderness. Tenderness is frequently found at the apices of spinal curves and not infrequently where one curve merges with another. Tenderness about spinous or transverse processes is usually of low intensity and suggests articular stress. Tenderness noted at the points of nerve exit from the spine and continuing in the pathway of the peripheral division of the nerves is a valuable aid in spinal analysis pointing to a foraminal lesion. However, the lack of tenderness is not a clear indication of lack of spinal dysfunction. Tenderness is a subjective symptom influenced by many individual structural, functional, and psychologic factors that can make it an unreliable sign. An area for clues sometimes overlooked is the presence and symmetry of lower-extremity pulses.
Keep in mind that lumbopelvic tenderness as well as pain can be referred from pelvic and lower abdominal viscera.
LUMBAR SUBLUXATION SYNDROMES
Functional revolts associated with subluxation syndromes can manifest as abnormalities in sensory interpretations and/or motor activities. These disturbances may be through one of two primary mechanisms: direct nerve disorders or be of a reflex nature.
Nerve Root Insults
Read the rest of this Full Text article now!
Enjoy the rest of Dr. Schafer’s Monographs at:


This is really a great article! I have referred this to some of the orthopedist I refer with. So many times if they can’t see something on an MRI or EMG study they try to shotgun their treatment. This is a great reminder of how complex the spine really can be.
Hi Russell
The Blog format leaves a lot to be desired.
A full-width version of this monograph is available at:
http://www.chiro.org/rc_schafer/Monograph_24.shtml
Thanks, I will refer to the full version.