The Swiss Chiropractic Practice-based Research Network: A Population-based Cross-sectional Study to Inform Future Musculoskeletal Research
SOURCE: Scientific Reports 2023 (Apr 6); 13 (1): 5655
OPEN ACCESS
Rahim Lalji, Léonie Hofstetter, Alice Kongsted, Viktor von Wyl, Milo A. Puhan & Cesar A. Hincapié
EBPI-UWZH Musculoskeletal Epidemiology Research Group,
University of Zurich and Balgrist University Hospital,
Forchstrasse 340, 8008,
Zurich, Switzerland.
FROM: BMJ Open 2022
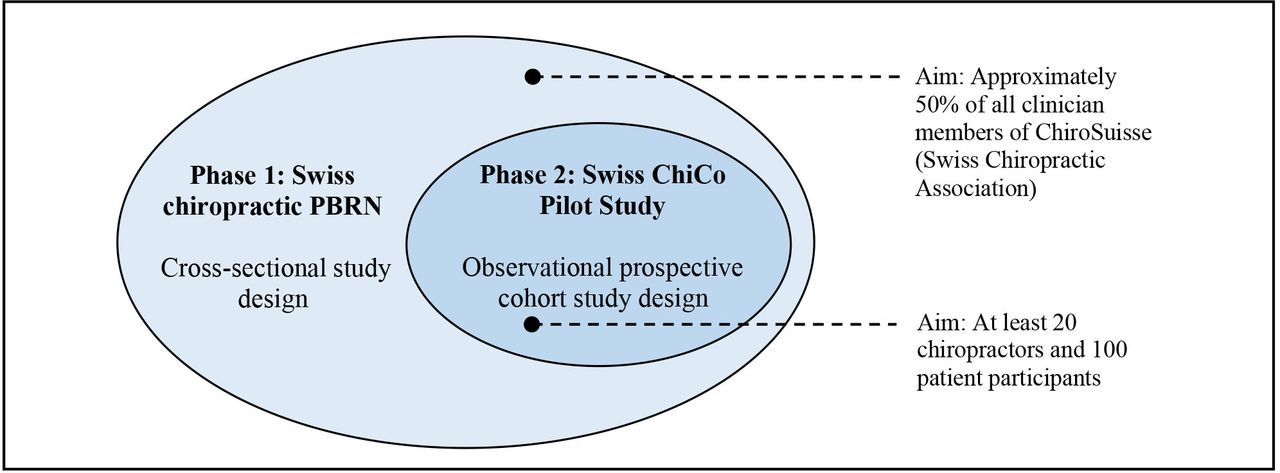
The Swiss chiropractic practice-based research network (PBRN) is a nationwide project developed in collaboration with patients, clinicians, and academic stakeholders to advance musculoskeletal epidemiologic research. The aim of this study was to describe the clinician population recruited and representativeness of this PBRN to inform future collaboration. A population-based cross-sectional study was performed. PBRN clinician characteristics were described and factors related to motivation (operationalised as VAS score ≥ 70) to participate in a subsequent patient cohort pilot study were assessed. Among 326 eligible chiropractors, 152 enrolled in the PBRN (47% participation). The PBRN was representative of the larger Swiss chiropractic population with regards to age, language, and geographic distribution. Of those enrolled, 39% were motivated to participate in a nested patient cohort pilot study. Motivation was associated with age 40 years or older versus 39 years or younger (OR 2.3, 95% CI 1.0–5.2), and with a moderate clinic size (OR 2.4, 95% CI 1.1–5.7) or large clinic size (OR 2.8, 95% CI 1.0–7.8) versus solo practice. The Swiss chiropractic PBRN has enrolled almost half of all Swiss chiropractors and has potential to facilitate collaborative practice-based research to improve musculoskeletal health care quality.
Trial registration: Swiss chiropractic PBRN
(ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05046249);
Swiss chiropractic cohort (Swiss ChiCo) pilot study
(ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05116020).
From the FULL TEXT Article:
Introduction
There are more articles like this @ our:
Musculoskeletal (MSK) pain conditions, such as neck pain and low back pain, are a leading cause of disability globally and are the most prevalent disease area which would benefit from rehabilitation. [1] One factor which may contribute to this disability burden is a lack of MSK health care quality. [2, 3] Examples of substandard clinical management of MSK pain include an overutilization of diagnostic imaging, the over prescription of opioids, and the potential underutilization of nonpharmacological approaches. [4–7] As a large proportion of MSK pain is managed in primary care, efforts to improve the quality of care in these settings, such as the development of practice-based research networks (PBRNs), may play an important role in identifying, studying, and addressing similar practice-based gaps. [8–10]


Leave A Comment