Multidisciplinary Integrative Care Versus Chiropractic Care for Low Back Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial
SOURCE: Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2022 (Mar 1); 30: 10
Gert Bronfort, Michele Maiers, Craig Schulz, Brent Leininger, Kristine Westrom, Greg Angstman & Roni Evans
University of Minnesota,
Mayo Building C504,
420 Delaware Street SE,
Minneapolis, MN, 55455, USA.
Read the 2 previous papers associated with this study:
Background: Low back pain (LBP) is influenced by interrelated biological, psychological, and social factors, however current back pain management is largely dominated by one-size fits all unimodal treatments. Team based models with multiple provider types from complementary professional disciplines is one way of integrating therapies to address patients’ needs more comprehensively.
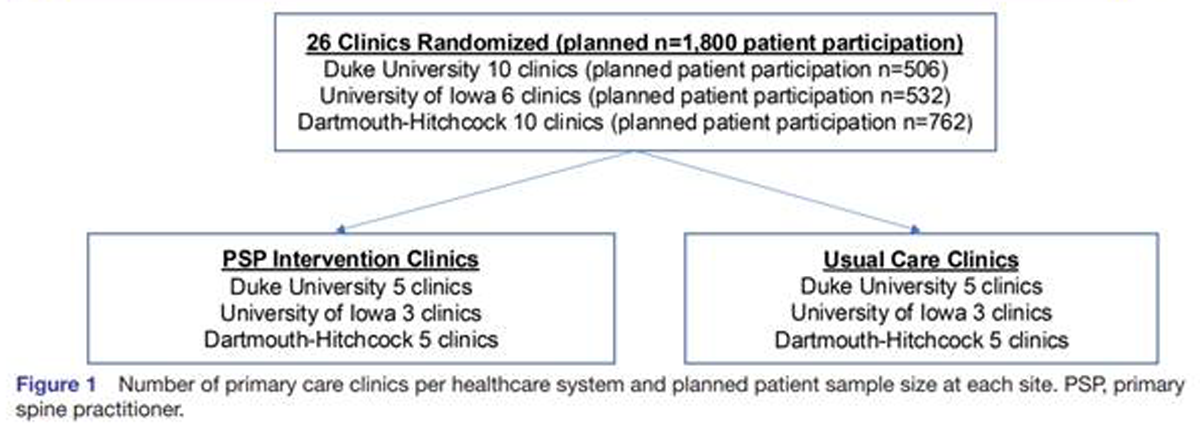
Methods: This parallel group randomized clinical trial conducted from May 2007 to August 2010 aimed to evaluate the relative clinical effectiveness of 12 weeks of monodisciplinary chiropractic care (CC), versus multidisciplinary integrative care (IC), for adults with sub-acute and chronic LBP. The primary outcome was pain intensity and secondary outcomes were disability, improvement, medication use, quality of life, satisfaction, frequency of symptoms, missed work or reduced activities days, fear avoidance beliefs, self-efficacy, pain coping strategies and kinesiophobia measured at baseline and 4, 12, 26 and 52 weeks. Linear mixed models were used to analyze outcomes.
There are more articles like this @ our:
Conclusions: Low back pain patients who received integrative care by a multidisciplinary integrative care team tended to have better outcomes than those who received chiropractic care. However, given the relatively small magnitude of between group differences and the extensive resources required to successfully manage and implement, the team based integrative care might not be worthwhile. More efficient models for addressing biopyschosocial care for low back pain should be explored with greater emphasis on addressing the full spectrum of related psychosocial mechanisms and ensuring equitable access for all.
Trial registration ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00567333
Keywords: Back pain; Chiropractic; Clinical trial; Integrative medicine; Multidisciplinary.





Leave A Comment