The Effect of Adding Forward Head Posture Corrective Exercises in the Management of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy: A Randomized Controlled Study
SOURCE: J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2015 (Feb 19) [Epub ahead of print]
Ibrahim M. Moustafa, PT, PhD, Aliaa A. Diab, PT, PhD
Assistant Professor,
Basic Science Department,
Faculty of Physical Therapy,
Cairo University, Giza, Egypt.
ibrahiem.mostafa@pt.cu.edu.eg
Objective The purpose of this study was to determine the immediate and long-term effects of a multimodal program, with the addition of forward head posture correction, in patients with chronic discogenic lumbosacral radiculopathy.
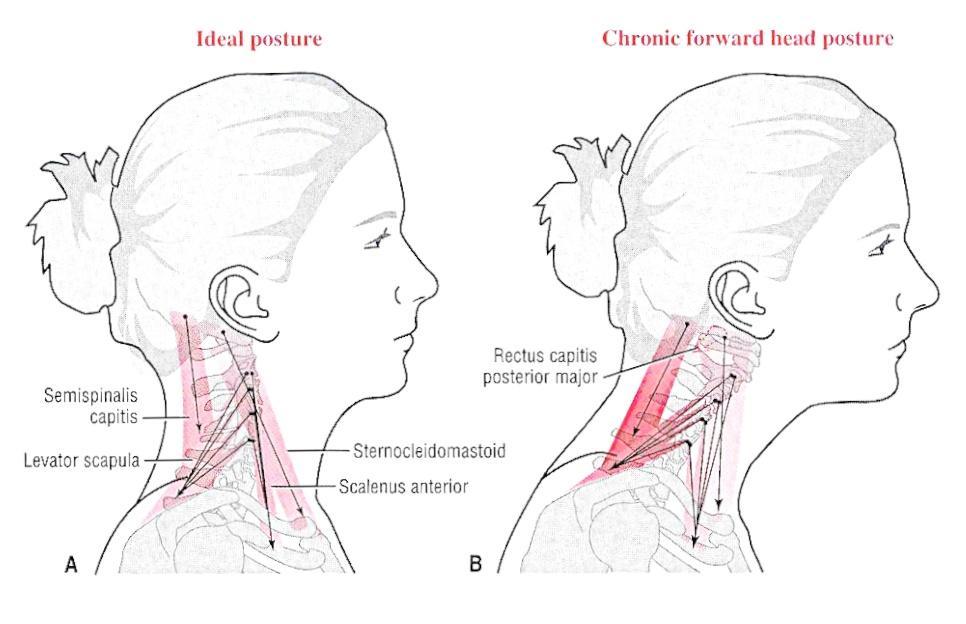
Methods This randomized clinical study included 154 adult patients (54 females) who experienced chronic discogenic lumbosacral radiculopathy and had forward head posture. One group received a functional restoration program, and the experimental group received forward head posture corrective exercises. Primary outcomes were the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI). Secondary outcomes included the anterior head translation, lumbar lordosis, thoracic kyphosis, trunk inclination, lateral deviation, trunk imbalance, surface rotation, pelvic inclination, leg and back pain scores, and H-reflex latency and amplitude. Patients were assessed at 3 intervals (pretreatment, 10-week posttreatment, and 2-year follow-up).
Results A general linear model with repeated measures indicated a significant group × time effect in favor of the experimental group on the measures of ODI (F = 89.7; P < .0005), anterior head translation (F = 23.6; P < .0005), H-reflex amplitude (F = 151.4; P < .0005), H-reflex latency (F = 99.2; P < .0005), back pain (F = 140.8; P < .0005), and leg pain (F = 72; P < .0005). After 10 weeks, the results revealed an insignificant difference between the groups for ODI (P = .08), back pain (P = .29), leg pain (P = .019), H-reflex amplitude (P = .09), and H-reflex latency (P = .098). At the 2-year follow-up, there were significant differences between the groups for all variables adopted for this study (P < .05).
There are more articles like this @ our:
Conclusions The addition of forward head posture correction to a functional restoration program seemed to positively affect disability, 3-dimensional spinal posture parameters, back and leg pain, and S1 nerve root function of patients with chronic discogenic lumbosacral radiculopathy.
From the FULL TEXT Article:
Introduction
Lumbosacral radiculopathy associated with disk herniation is one of the most common health-related complaints. [1] It is a disorder associated with delayed recovery, persistent disability, and increased health care utilization and costs. [2] Despite the high prevalence of this condition, [3] its conservative treatment has been a challenge [4] because there is no strong evidence for the effectiveness of most treatments, particularly in long-term management. [5]
Read the rest of this article here!



Leave A Comment