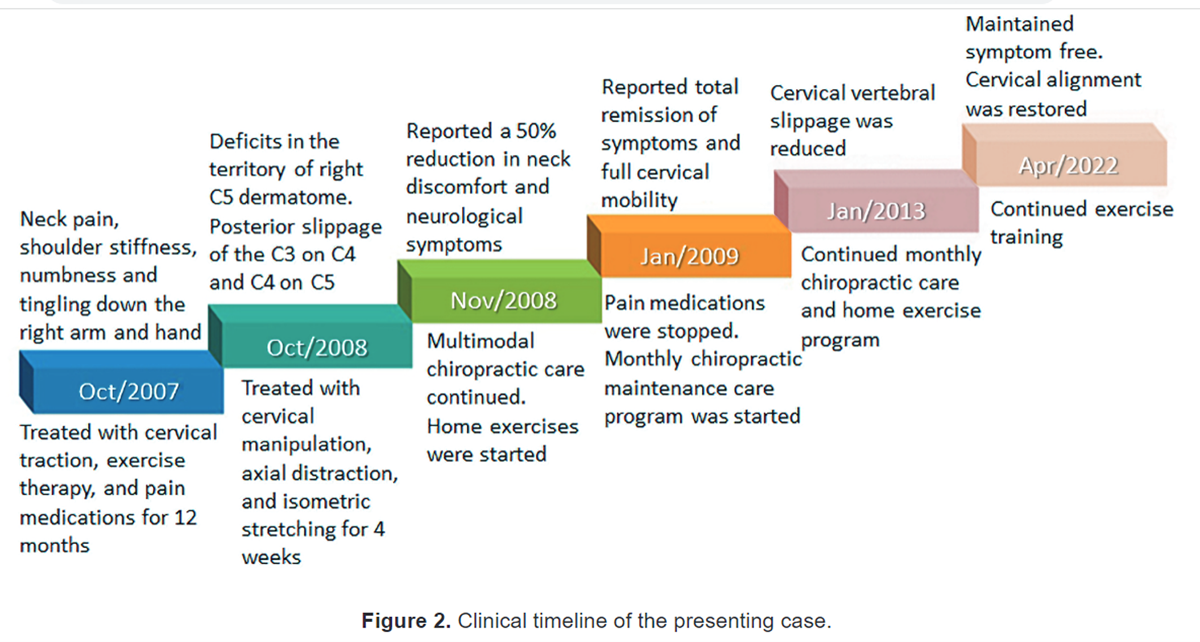
Symptomatic Reactions, Clinical Outcomes and Patient Satisfaction Associated with Upper Cervical Chiropractic Care: A Prospective, Multicenter, Cohort Study
SOURCE: BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 (Oct 5); 12: 219
Kirk Eriksen, Roderic P Rochester, and Eric L Hurwitz
Chiropractic Health Institute, PC, Clinic Director, 2500 Flowers Chapel Road, Dothan, AL 36305, USA. drkirke@graceba.net
BACKGROUND: Observational studies have previously shown that adverse events following manipulation to the neck and/or back are relatively common, although these reactions tend to be mild in intensity and self-limiting. However, no prospective study has examined the incidence of adverse reactions following spinal adjustments using upper cervical techniques, and the impact of this care on clinical outcomes.
METHODS: Consecutive new patients from the offices of 83 chiropractors were recruited for this practice-based study. Clinical outcome measures included:
- Neck pain disability index (100-point scale),
- Oswestry back pain index (100-point scale),
- 11-point numerical rating scale (NRS) for neck, headache, midback, and low back pain,
- treatment satisfaction, and
- Symptomatic Reactions (SR).
Data were collected at baseline, and after approximately 2 weeks of care. A patient reaching sub-clinical status for pain and disability was defined as a follow-up score <3 NRS and <10%, respectively. A SR is defined as a new complaint not present at baseline or a worsening of the presenting complaint by >30% based on an 11-point numeric rating scale occurring <24 hours after any upper cervical procedure.
RESULTS: A total of 1,090 patients completed the study having 4,920 (4.5 per patient) office visits requiring 2,653 (2.4 per patient) upper cervical adjustments over 17 days. Three hundred thirty- eight (31.0%) patients had SRs meeting the accepted definition. Intense SR (NRS ≥8) occurred in 56 patients (5.1%). Outcome assessments were significantly improved for neck pain and disability, headache, mid-back pain, as well as lower back pain and disability (p <0.001) following care with a high level (mean = 9.1/10) of patient satisfaction. The 83 chiropractors administered >5 million career upper cervical adjustments without a reported incidence of serious adverse event.
CONCLUSIONS: Upper cervical chiropractic care may have a fairly common occurrence of mild intensity SRs short in duration (<24 hours), and rarely severe in intensity; however, outcome assessments were significantly improved with less than 3 weeks of care with a high level of patient satisfaction. Although our findings need to be confirmed in subsequent randomized studies for definitive risk-benefit assessment, the preliminary data shows that the benefits of upper cervical chiropractic care may outweigh the potential risks.
From the FULL TEXT Article:
Discussion:
This study provides the incidence of Symptomatic Reactions (SRs) related to upper cervical techniques (UCT) and the improvement in clinical outcomes following this form of spinal care. The preponderance of the evidence shows that major complications resulting from chiropractic care are very rare, although transient discomfort and other minor side effects of chiropractic care are common. Various prospective studies have shown about 30% to 60% of patients receiving SMT experience minor side effects shortly after treatment [1-12,38]. Local discomfort in the treatment area accounts for half to two-thirds of the reactions. Other effects such as radiating symptoms, headaches, tiredness/fatigue each account for about 10% of SRs. Side effects such as nausea, dizziness and other symptoms are rare and most studies show that each of these comprise of 5% or less of reported symptoms. The majority of reactions have been reported to begin within 24 hours of the treatment visit and to resolve in less than 24 hours.
risks.




Leave A Comment